
- Background -
Vaccine storage is a critical step in ensuring the safety and efficacy of vaccines. Proper storage conditions guarantee the quality of drugs and vaccines, preventing temperature fluctuations and humidity issues that could lead to losses. The stability of storage environments is crucial not only during the logistics and distribution process but also for healthcare facilities and pharmacies.
- Challenges -
Temperature variations directly impact the quality of vaccines. Most vaccines must be stored within a temperature range of +2°C to +8°C (+36°F to +46°F). Temperature fluctuations can result in vaccine degradation and loss of effectiveness.
Storing different types of vaccines can present challenges as individual products may have unique storage requirements, including specific temperature ranges. The following are best practices for storing some popular vaccines:
Vaccine | Storage Temperature |
Gardasil (HPV vaccine) | +2°C ~+8°C (+36°F~+46°F) |
Dengvaxia (Dengue Vaccine) | +2°C ~+8°C (+36°F~+46°F) |
M-M-R II (Measles, Mumps, Rubella Vaccine) | -50°C~ 8°C (-58°F~46°F) |
Prevnar 13(Pneumonia Vaccine) | +2°C ~+8°C (+36°F~+46°F) |
ProQuad (Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Varicella Vaccine) | -50°C~-15°C (-58°F~5°F) |
Influenza vaccines | +2°C ~+8°C (+36°F~+46°F) |
COVID-19 (Novavax) | +2°C ~+8°C (+36°F~+46°F) |
COVID-19 (Moderna) | -25°C~-15°C (-13°F~+5°F) |
In the past, temperature and humidity in vaccine storage and transportation relied on manual monitoring and record-keeping. This approach is susceptible to human errors and does not provide real-time alerts for temperature and humidity abnormalities. Additionally, monitoring these conditions for large-scale vaccine storage facilities is time-consuming and complex, requiring additional manpower and resources.

Refrigerated storage
equipment failure

Lack of early
warning mechanisms

Time-wasted
manual recording
- Solution -
Daily Temperature Checks
It is recommended to check and record the lowest and highest temperatures of refrigerators at the start of each workday to identify any temperature deviations or potential issues.
Plan for Power Outages
Power outages are a major risk to vaccine quality. Planning is essential to address this issue, including backup power sources, alternative storage options, regular maintenance checks, and procedures to maintain temperature control during power interruptions.
Rotate Vaccines Based on Expiry Dates
Rotating vaccine inventory based on expiry dates ensures the utilization of older vaccines first, minimizing unnecessary wastage and reducing the risk of administering expired vaccines.
Equip with MOCREO Temperature Monitoring System
The MOCREO remote temperature monitoring system features wireless sensors, a data transmission hub, and the MOCREO monitoring platform. If anything unusual occurs, the system can send notifications, emails, and alerts. This can improve the reliability, safety, and effectiveness of the vaccine storage process, reduce vaccine losses, and ensure that vaccines maintain their quality and effectiveness when needed.
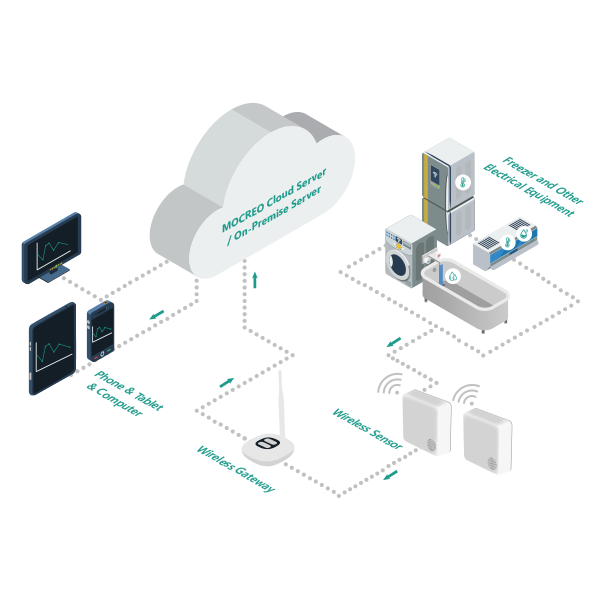
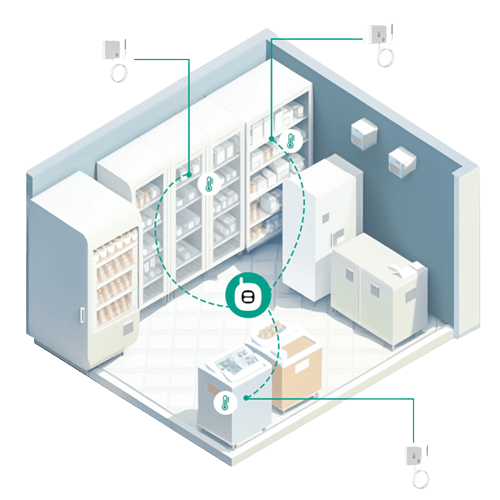
24/7 Real-Time Monitoring
With the MOCREO application/portal, you can have constant access to the temperature status of any refrigerator, anytime and anywhere.
Flexible Notification Options
Through App notifications, email, or local alarms, staff can make a quick response, minimizing the risks and preventing medical resource loss.
Automated Regulatory Logs & Reporting
Eliminate the need for manual temperature data recording by staff, saving time, avoiding data errors, and optimizing workforce efficiency.
Multi-Device Access
Multiple users or devices can easily log into the same account for monitoring and alerts, enabling shared responsibility for regular facility monitoring and enhancing monitoring capabilities.
- Future -
Proper vaccine storage is crucial for protecting public health. With advancements in technology, ensuring the safe and effective storage of these sensitive items becomes more feasible. Investing in these technologies is not only an investment in public health but also a safeguard for future health security.
